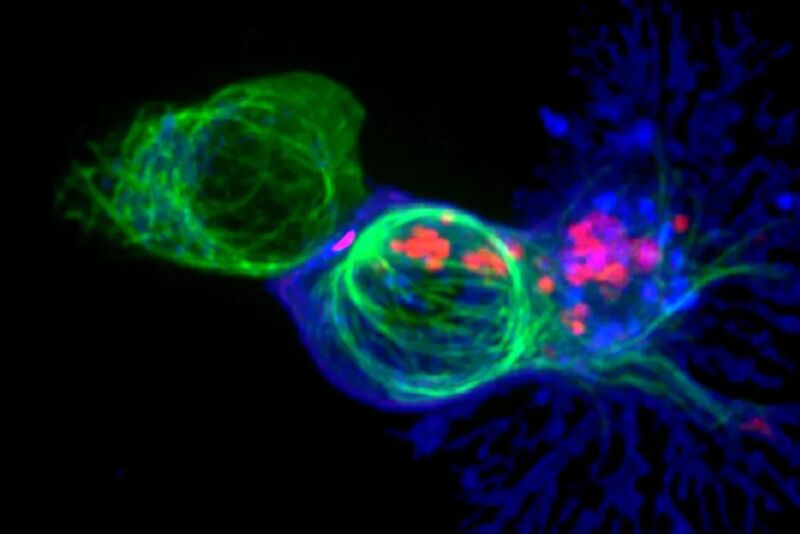
Enlarge / This microscopy image shows a cytotoxic T cell (blue) attacking a cancer cell (green) by releasing toxic chemicals (red). (credit: Alex Ritter, Jennifer Lippincott Schwartz, and Gillian Griffiths/National Institutes of Health)
A key function of our immune system is to detect and eliminate foreign pathogens such as bacteria and viruses. Immune cells like T cells do this by distinguishing between different types of proteins within cells, which allows them to detect the presence of infection or disease.
A type of T cell called cytotoxic T cells can recognize the mutated proteins on cancer cells and should therefore be able to kill them. However, in most patients, cancer cells grow unchecked despite the presence of T cells.
The current explanation scientists have as to why T cells fail to eliminate cancer cells is because they become “exhausted.” The idea is that T cells initially function well when they first face off against cancer cells, but gradually lose their ability to kill the cancer cells after repeated encounters.
Read 13 remaining paragraphs | Comments
Ars Technica - All contentContinue reading/original-link]




