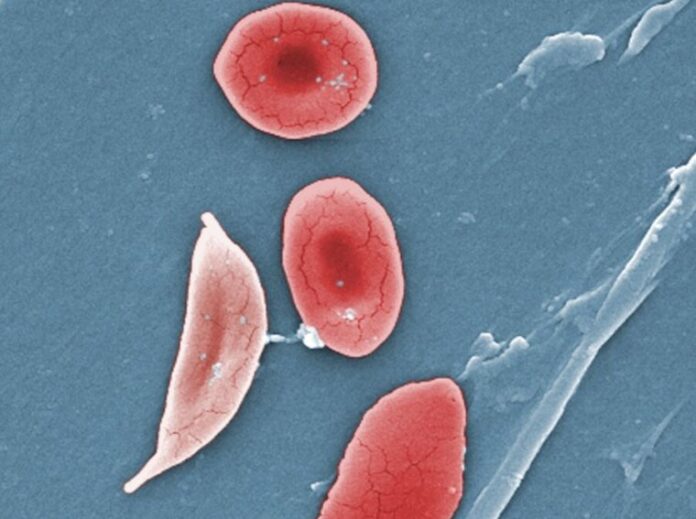
Enlarge / This digitally colorized scanning electron micrograph (SEM) revealed some of the comparative ultrastructural morphology between normal red blood cells (RBCs), and a sickle cell RBC (left) found in a blood specimen of an 18-year-old female patient with sickle cell anemia. (credit: CDC)
The Food and Drug Administration on Friday approved two gene therapies to treat sickle cell disease, one of the which is the first CRISPR/Cas9-based treatment to win regulatory approval in the US.
The announcement is a landmark in the treatment of sickle cell disease, a devastating condition in which red blood cells deform into a sickle shape and clog up blood vessels. Sickle cell disease affects around 100,000 people in the US, most commonly African Americans. It leads to anemia, vaso-occlusive events and crises (painful episodes in which small blockages starve tissue of oxygen), strokes, progressive and irreversible organ damage, decreased quality of life, and early death.
Until today, treatments have been limited. A bone marrow transplant from a genetically matched sibling can cure the condition more than 90 percent of the time, but only around 20 percent of people with the disease have such a genetically matched sibling donor. There are also multiple drugs available and supportive care, but these mainly reduce the severity of the disease. The new gene therapy treatments, on the other hand, have shown to be highly effective at preventing vaso-occlusive events and crises.
Read 8 remaining paragraphs | Comments
Ars Technica - All contentContinue reading/original-link]